Let's Workshop: Keyes LDR Sensor Module Black Version
Posted by Sebastian Karam on
Here is a quick introduction to using the Keyes LDR sensor module. Hopefully it will provide you with the confidence to intergrate light sensing into your project.
This example will demonstrate the use of an Arduino UNO in monitoring an analog pin over the range of light levels that an LDR responds to.
Components
- 1pcs Arduino UNO or Compatible - LCAA100005
- 1pcs Keyes LDR Sensor Module - BDAA100008
- 3pcs Male to Female Jumper Cables - GBAA100002
Wiring
Wire the one of the two boards to the Arduino as can be seen in the images below, taking care to match the pin numbers.
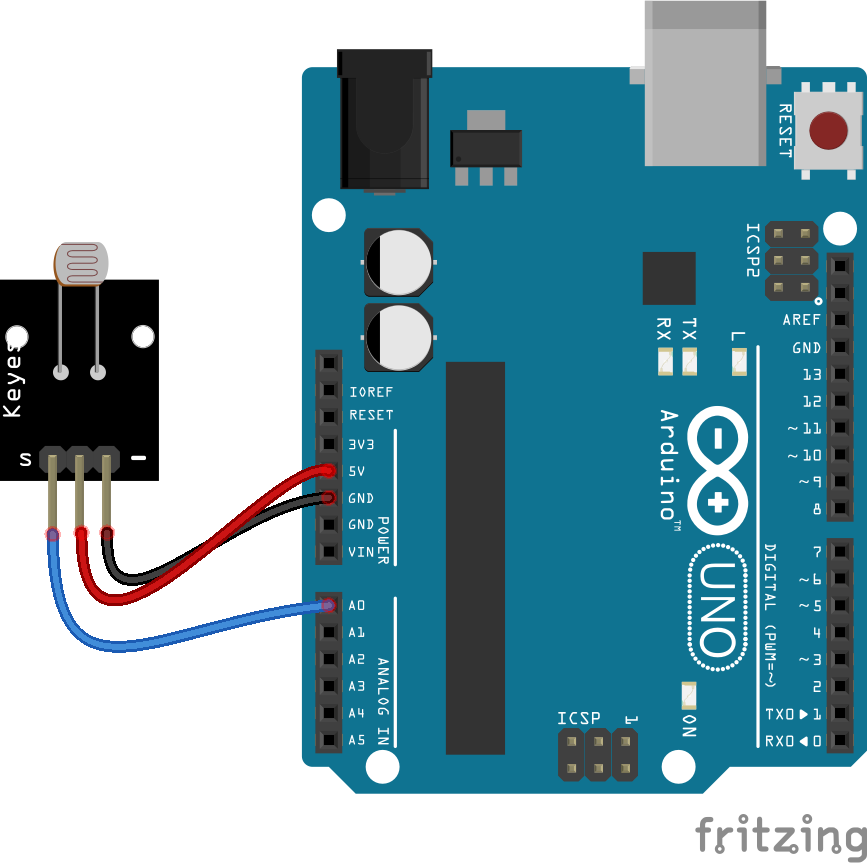
Coding
The code consists of a definition, setup and loop. First the A0 pin is assigned followed by a varaiable to store the value read. This allows easier use later in your program. A setup informs the system that the pin is an input is an input and then lauches the serial connection. Next we enter the loop, where the value on the pin is read and stored in the variable declared earlier. Following that we send it to the serial monitor so that the value can be read on the screen.
Load the code below into the Arduino IDE and upload it to your board.
/*
A simple program designed to setup and demonstrate the Keyes LDR Sensor Module - BDAA100008.
The program monitors a connected analog pin and outputs the value to the
serial monitor.
modified 29th August 2019
by Sebastian Karam - Flux Workshop
*/
int analogApin = 0; // define OUT signal pin
int analogA; // define variable to store value read from pin
void setup() {
pinMode(analogApin, INPUT); // set the OUT signal pin as an input
Serial.begin(9600); // launch the serial monitor
Serial.println("Flux Workshop Example");
}
void loop() {
analogA = analogRead(analogApin); // read the voltage level on the A0
Serial.println((String)"Light level: " + analogA); // send the result to the serial monitor
delay(200); // pause for a moment before repeating
}
Running
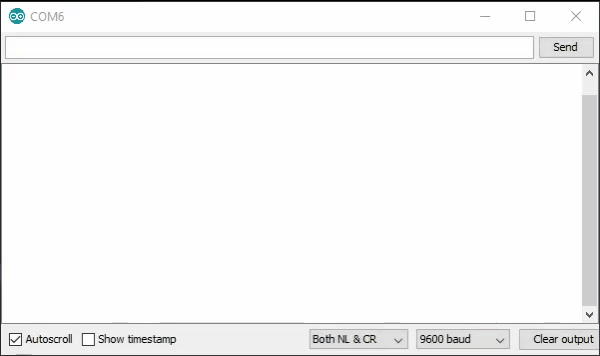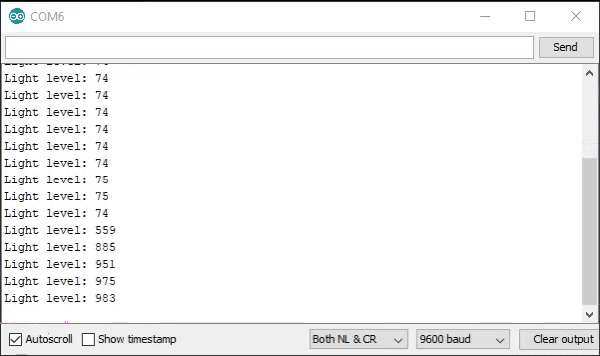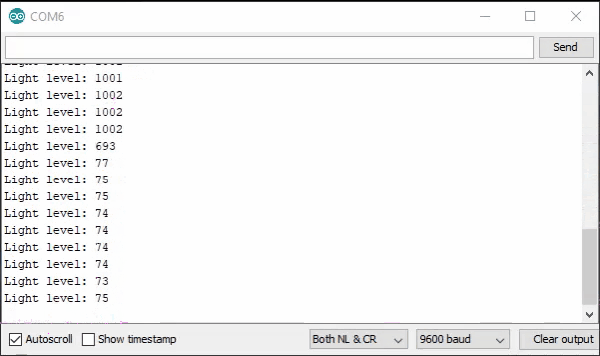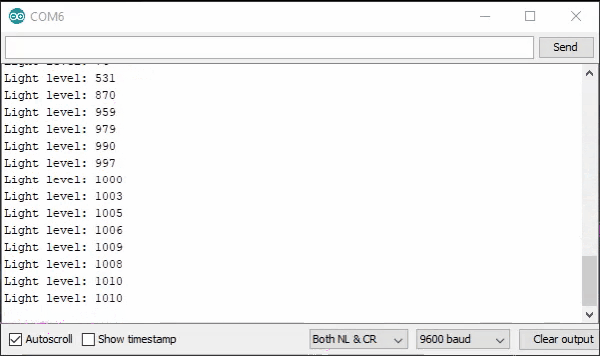
With the board loaded with the program and all the connections made the serial monitor will produce an output like the one seen below. In this case the sensor is in bright sunlight before it is covered by a cup. I then repeat a few more times, as the number change is satisfying.
What to try next?
- Use the output to monitor sunrise and sunset.
- As the sensor reacts to reflected light, line sensing should be possible. Ideal as the basis for a line following robot.
